springframework-course
Unit Testing Rest API using JUnit 5
Now that we’ve completed the Spring Boot API implementation, let’s look at how we can unit test it with JUnit 5 and Mockito.
Test JPA Repository using @DataJpaTest
Let’s start with BookRepository. To improve testing functionality for JPA repositories, Spring Boot includes the @DataJpaTest annotation.
By annotating the unit test class with @DataJpaTest, we can instruct Spring to automatically configure JPA repositories.
Step 1: Create BookRepositoryTest class in the below location /src/test/java/com/springcourse/learnspringboot/book
@DataJpaTest
public class BookRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
}
As we can see, we autowired bookRepository without any further configuration.
By default, @DataJpaTest uses an embedded in-memory database under the hood.
Please note that with JUnit 5, test classes and test methods are not required to be public.
Step 2: Now, let’s create a test case for each method:
@DataJpaTest
public class BookRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@Test
void shouldReturnAllBooksList() {
// When
List<Book> books = this.bookRepository.findAll();
// Then
assertEquals(3, books.size());
}
@Test
void shouldReturnBookById() {
// When
Optional<Book> books = this.bookRepository.findById(1001L);
// Then
assertTrue(books.isPresent());
}
@Test
void shouldCreateABook() {
// Given
Book bookOne = new Book();
bookOne.setId(1004L);
bookOne.setTitle("AWS Lambda");
bookOne.setAuthor("Mahi");
bookOne.setIsbn("ISBN4");
// When
Book saveBook = this.bookRepository.save(bookOne);
List<Book> books = this.bookRepository.findAll();
// Then
assertNotNull(saveBook);
assertEquals(4, books.size());
}
@Test
void shouldDeleteABookById() {
// When
this.bookRepository.deleteById(1001L);
Optional<Book> books = this.bookRepository.findById(1001L);
// Then
assertFalse(books.isPresent());
}
}
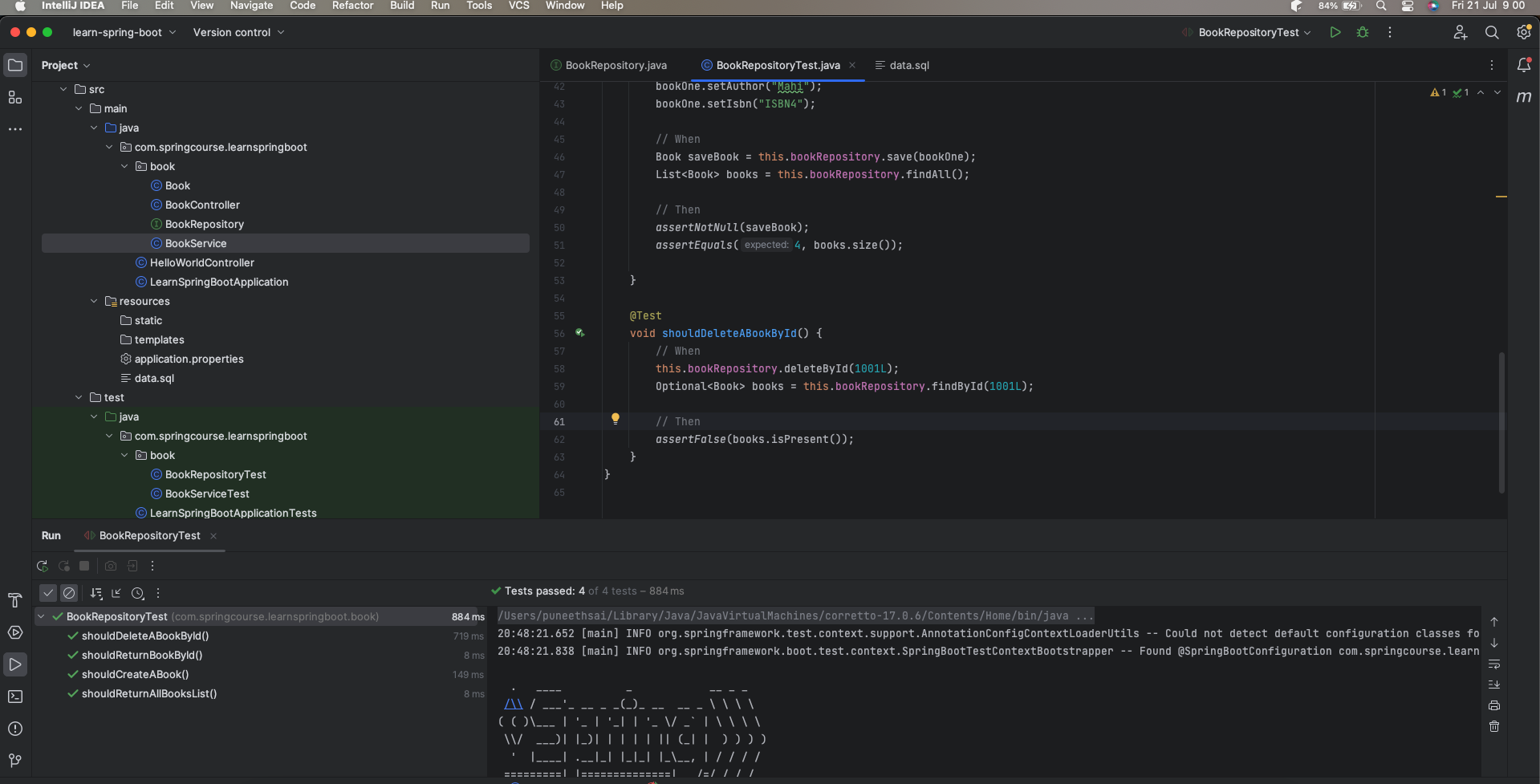
As shown above, we used JUnit 5 assertions to verify that everything works as expected for each method. Here is the result screen
Step 3: Run the BookRepositoryTest class
Test Service Layer using Mockito
Next, we are going to test our service BookService. Since it uses BookRepository as a dependency, we will need to mock it first.
Simply put, Mockito is a powerful mocking framework that takes testing to the next level.
Fortunately, JUnit 5 comes with a ready-to-use extension model that supports Mockito.
To enable Mockito integration, we need to annotate our test class with the @ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class) annotation:
Step 1: Create BookServiceTest in the below location /src/test/java/com/springcourse/learnspringboot/book
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
public class BookServiceTest {
@Mock
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@InjectMocks
private BookService bookService;
}
-
@Mock allows us to create and inject a mock of BookRepository
-
@InjectMocks is used to create an instance of our service BookService so that we can test it
Step 2: Now, let’s exemplify the use of Mockito and JUnit 5 to test our service:
package com.springcourse.learnspringboot.book;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.mockito.InjectMocks;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.junit.jupiter.MockitoExtension;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.verify;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
public class BookServiceTest {
@Mock
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@InjectMocks
private BookService bookService;
@Test
void shouldReturnAllBooks() {
// Given
Book bookOne = new Book(1004L, "Book4", "Author4", "ISBN4");
// When
when(bookRepository.findAll()).thenReturn(List.of(bookOne));
List<Book> books = bookService.getAllBooks();
// Then
assertThat(books).hasSize(1);
verify(this.bookRepository).findAll();
}
@Test
void shouldReturnBookById() {
// Given
Book bookOne = new Book(1004L, "Book4", "Author4", "ISBN4");
// When
when(bookRepository.findById(1004L)).thenReturn(Optional.of(bookOne));
Optional<Book> returnedBook = Optional.ofNullable(this.bookService.getBookById(1004L));
// Then
assertEquals(bookOne.getId(), returnedBook.get().getId());
verify(this.bookRepository).findById(1004L);
}
@Test
void shouldCreateANewBook() {
// Given
Book bookOne = new Book(1004L, "Book4", "Author4", "ISBN4");
// When
this.bookService.saveBook(bookOne);
// Then
verify(this.bookRepository).save(bookOne);
}
@Test
void shouldDeleteABook() {
// When
this.bookService.deleteBook(1004L);
// Then
verify(this.bookRepository).deleteById(1004L);
}
}
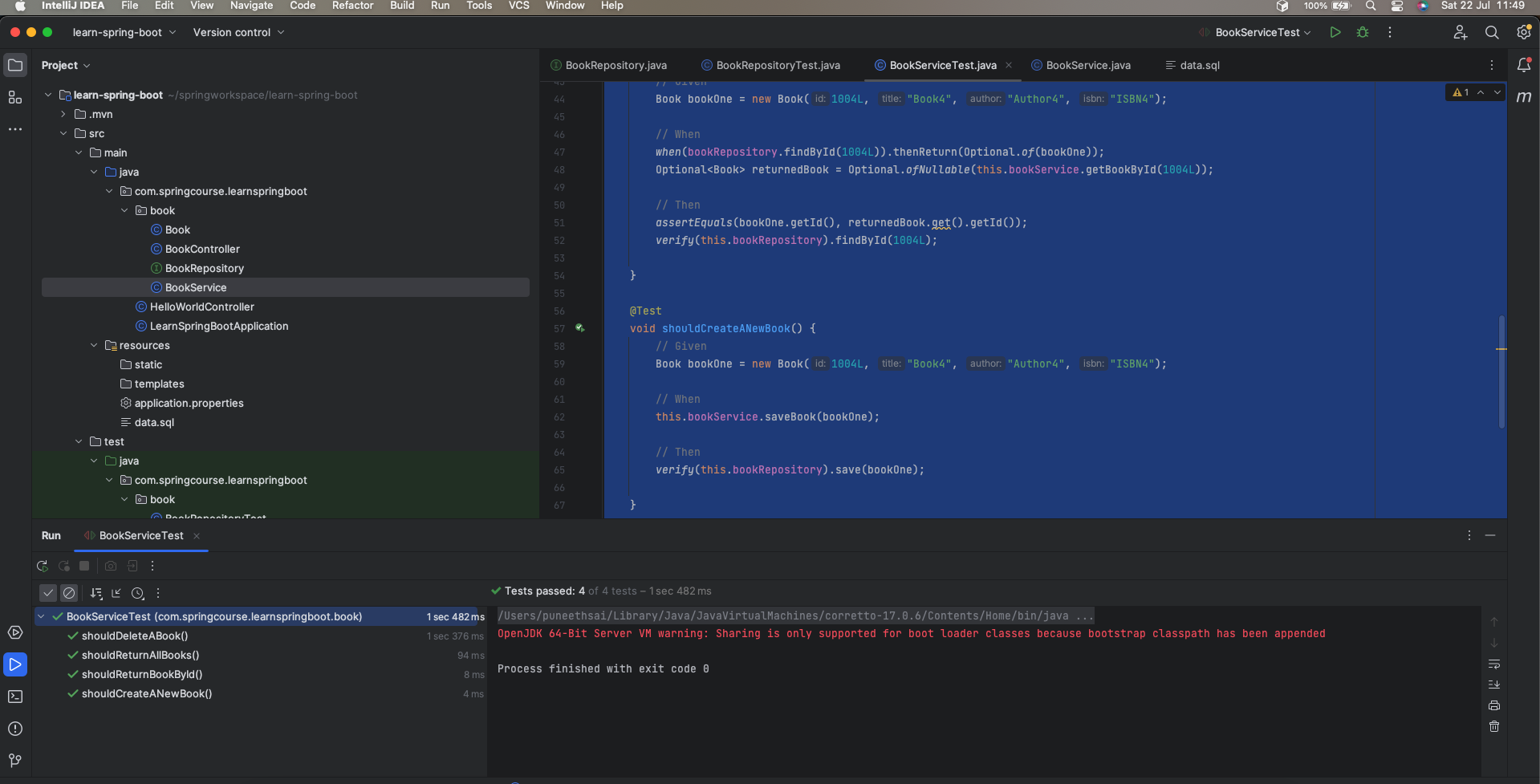
We utilised verify() in conjunction with JUnit 5 assertions to ensure that employeeRepository methods are correctly triggered when employeeService methods are called.
Step 3: Run the BookServiceTest class
Testing Controller Endpoints
After we’ve tested the JPA repository and the service layer, it’s time to test the Spring controller.
There are numerous approaches to evaluating a rest API. Let us examine each possibility in detail.
Using @WebMvcTest
Spring Boot offers @WebMvcTest to focus only on testing Spring MVC web components such as Rest APIs.
By default, tests annotated with @WebMvcTest will automatically configure MockMvc.
MockMvc, as the name suggests, offers mocking and testing support for Spring web controllers.
Step 1: So, let’s see how we can use it to test our API or BookController:
@WebMvcTest(BookController.class)
public class BookControllerTest {
@MockBean
private BookService bookService;
@MockBean
private BookRepository repository;
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
}
As we can see, @WebMvcTest lets us specify the controller we want to test.
Please note also that we used @MockBean to create a mock of BookService and BookRepository and add it into the application context.
Now, let’s add a test case for each API’s endpoint:
package com.springcourse.learnspringboot.book;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.hasSize;
import static org.mockito.ArgumentMatchers.any;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.*;
@WebMvcTest(BookController.class)
public class BookControllerTest {
@MockBean
private BookService bookService;
@MockBean
private BookRepository repository;
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
// GET Operation
@Test
void shouldReturnBooks() throws Exception {
Book bookOne = new Book(1004L, "Book4", "Author4", "ISBN4");
when(bookService.getAllBooks()).thenReturn(List.of(bookOne));
when(repository.findAll()).thenReturn(List.of(bookOne));
mockMvc.perform(get("/books"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$", hasSize(1)))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$[0].id").value("1004"))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$[0].title").value("Book4"))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$[0].author").value("Author4"));
}
// POST Operation
@Test
void shouldCreateABook() throws Exception {
Book bookOne = new Book(1004L, "Book4", "Author4", "ISBN4");
when(bookService.saveBook(any(Book.class))).thenReturn(bookOne);
when(repository.save(any(Book.class))).thenReturn(bookOne);
mockMvc.perform(post("/books")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content("{ \"title\": \"Book4\", \"author\": \"Author4\", \"isbn\": \"ISBN4\" }"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.title").value("Book4"));
}
// DELETE Operation
@Test
void shouldRemoveBookById() throws Exception {
Book bookOne = new Book(1004L, "Book4", "Author4", "ISBN4");
when(bookService.saveBook(any(Book.class))).thenReturn(bookOne);
when(repository.save(any(Book.class))).thenReturn(bookOne);
when(bookService.getBookById(1004L)).thenReturn(bookOne);
when(repository.findById(1004L)).thenReturn(Optional.of(bookOne));
mockMvc.perform(delete("/books/{id}", 1004L))
.andExpect(status().isNoContent());
}
}
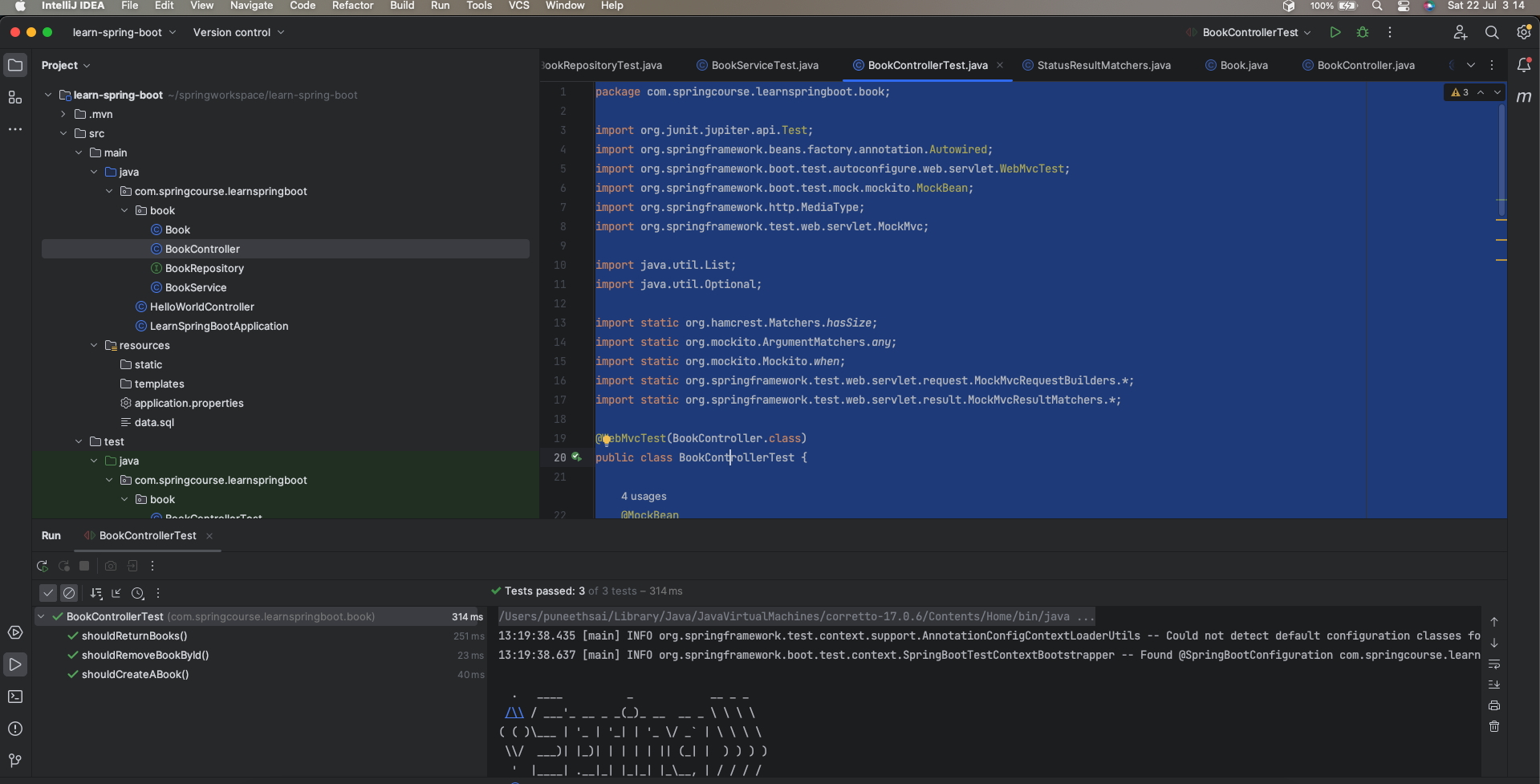
- MockMvc comes with the perform() method that we can use to test web request methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE
- andExpect allows us to assert the returned HTTP response
Step 3: Run the BookControllerTest class
Conclusion
We covered how to utilise JUnit 5 to unit test Spring Boot rest APIs.
-
First, we illustrated how to use
@DataJpaTestto test the JPA repositories. -
Then, we demonstrated how to use
Mockitoto mimic objects in order to provide testing for business services. -
Finally, we demonstrated how to use
MockMvcto test API endpoints.