springframework-course
Inversion of Control
Inversion of Control (IoC) is a core principle of the Spring Framework. It refers to the concept where the control of object creation and lifecycle management is shifted from the application code to a container or framework. The Spring container takes responsibility for instantiating, configuring, and managing objects (beans) based on their definitions and dependencies.
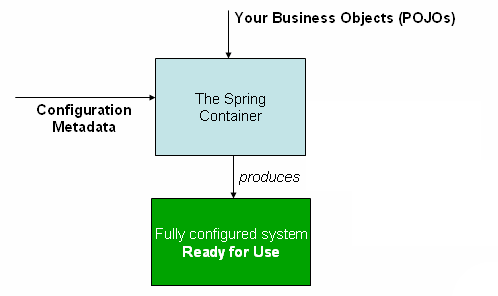
Source: Spring Framework Documentation
Here’s an example to illustrate IoC in the Spring Framework:
Consider a basic application with two classes, UserService and UserRepository, where UserService is dependent on UserRepository. Spring annotations will be used to configure the IoC container and handle dependencies.
Step 1: Define the UserRepository class
package com.springcourse.learnspring.springcore.ioc;
@Repository
public class UserRepository {
public void saveUser(User user) {
// Save user to the database
}
}
Step 2: Define the UserService class and inject the UserRepository dependency
package com.springcourse.learnspring.springcore.ioc;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
public UserService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
public void createUser(User user) {
// Perform user createUser logic
userRepository.saveUser(user);
}
}
Step 3: Configure the Spring IoC container using annotations
package com.springcourse.learnspring.springcore.ioc;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.springcourse.learnspring.springcore.ioc")
public class AppConfig {
// Configuration details
}
Step 4: Create a main class to bootstrap the Spring container:
package com.springcourse.learnspring.springcore.ioc;
public class InversionOfControlApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// Access the UserService bean and perform operations
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
User user = new User("Steve Jobs");
userService.createUser(user);
}
}
In this example, we use the @Repository annotation on the UserRepository class to indicate that it is a Spring-managed component responsible for data access.
Similarly, we use the @Service annotation on the UserService class to mark it as a Spring-managed service component.
The @Autowired annotation in the constructor of UserService indicates that Spring should inject an instance of UserRepository when creating the UserService bean. The @Autowired annotation can also be applied to fields or setter methods.
The @Configuration annotation on the AppConfig class signifies that it is a configuration class for the Spring container. The @ComponentScan annotation with the specified base package tells Spring to scan and detect components within that package.
Finally, in the main method of the InversionOfControlApp class, we create an instance of AnnotationConfigApplicationContext using the AppConfig class, which initializes the Spring IoC container. We retrieve the UserService bean from the container and invoke the createUser method.
With these annotations and configuration, Spring manages the creation and injection of dependencies, allowing you to focus on implementing the business logic in your application.